Concurrent Collection에 대해 정리가 필요할거같아 작성하였습니다.
Concurrent Collection이란?
Concurrent Collectioin은 Java5때 Thread Pool과 같이 도입된 Collection이며 다중 스레드 환경에서 발생할 수 있는 경합 조건 및 동기화 문제를 해결하기 위해 설계되었으며, java.util.concurrent 패키지 내에 포함되어 있습니다.
Concurrent Collection의 종류
Concurrent Collection의 종류는 대략적으로 다음과 같습니다.
- CopyOnWriteArrayList
- ConcurrentHashMap
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue
- LinkedBlockingQueue
- LinkedBlockingDeque
- ConcurrentSkipListMap
- ConcurrentSkipListSet
그외 여러가지가 있는데 그동안 중점적으로 공부한 내용을 바탕으로 몇몇 Collection들의 자세히 살펴보겠습니다.
CopyOnWriteArrayList
CopyOnWriteArrayList는 모든 쓰기 작업시 원본 배열에 있는 요소를 복사하여 새로운 임시 배열을 만들고, 이 임시 배열에 쓰기 동작을 수행한후 원본 배열을 갱신합니다. 따라서 이러한 작업 과정에서 동시성을 보장하기위하여 쓰기 작업시 Lock을 걸게됩니다.
하지만 이러한 Lock은 쓰기 작업의 성능을 저하시킵니다. Lock을 획득하는 동안에는 다른 스레드는 해당 List에 접근할수 없기 때문에 쓰기 작업이 빈번하게 발생하는경우 성능에 문제가 발생할수 있습니다.
public void add(int index, E element) {
synchronized (lock) {
Object[] es = getArray();
int len = es.length;
if (index > len || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBounds(index, len));
Object[] newElements;
int numMoved = len - index;
if (numMoved == 0)
newElements = Arrays.copyOf(es, len + 1);
else {
newElements = new Object[len + 1];
System.arraycopy(es, 0, newElements, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(es, index, newElements, index + 1,
numMoved);
}
newElements[index] = element;
setArray(newElements);
}
}
위의 코드는 CopyOnWriteArrayList의 add 메소드입니다. 보시면 add 작업을 진행할때 Synchronized 블록으로 Lock을 걸고 배열을 Copy하는 작업을 진행하는걸 볼수 있습니다.
ConcurrentHashMap
다음은 ConcurrentHashMap입니다.
구글링하게 되면 많이 볼수 있는데 Java5가 아닌 Java8 기준으로 바뀐 동작방식을 정리해 보았습니다.
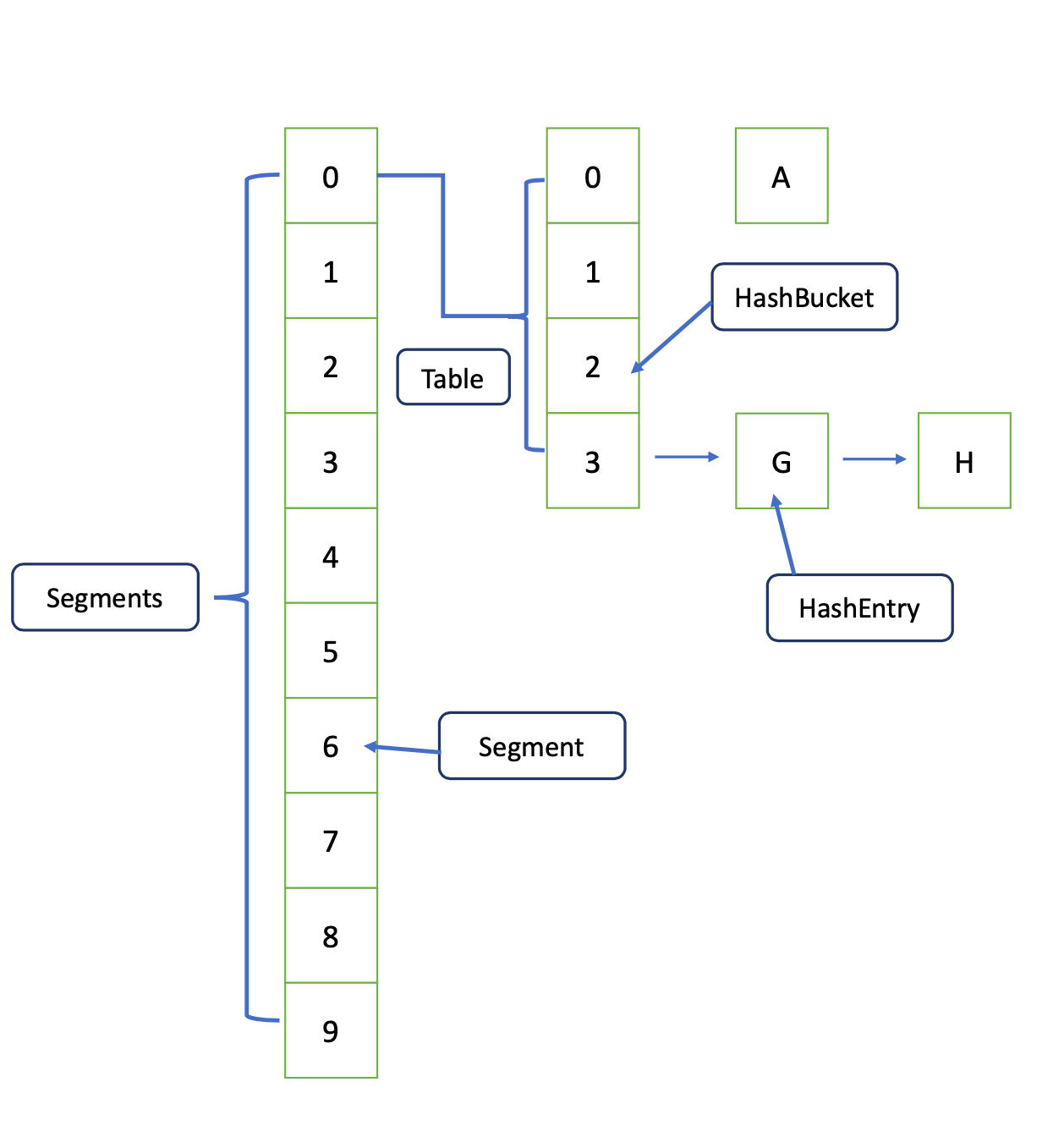
ConcurrentHashMap은 내부적으로 해시 버킷(Hash Bucket)이라는 구조 ( Key-Value쌍을 저장하는 공간)를 사용합니다.
과거에는 segment를 locking하는 방법을 사용하였으나 현재는 이러한 해시버킷에 대해 locking을 획득하여 동기화를 수행합니다.
위 내용을 코드를 통해 자세히 설명해보겠습니다.
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; K fk; V fv;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// 여기서 key의 hash code에 대한 버킷이 비어있다면 key-value쌍을 추가합니다.
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else if (onlyIfAbsent // check first node without acquiring lock
&& fh == hash
&& ((fk = f.key) == key || (fk != null && key.equals(fk)))
&& (fv = f.val) != null)
return fv;
else { // 이미 해시버킷에 노드가 존재하는 경우
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
else if (f instanceof ReservationNode)
throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update");
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
// 해시버킷에 저장된 노드의수가 일정 수준 이상 많아지면 해당 해시버킷을 이진트리로 변환합니다
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
버킷 배열을 순회하는 for문을 돌면서 버킷 배열이 null 이거나 비어있으면 버킷 배열을 초기화합니다.
그리고 key의 hashcode에 대한 버킷이 비어있다면 key-value쌍을 CAS 알고리즘을 사용하여 추가하게 됩니다.
비어있지 않고 해시버킷에 노드가 존재하는 경우에는 Synchronized 키워드 블록을 사용하여 하나의 스레드만 접근할수 있도록 Lock을 걸게 됩니다.
해시버킷에 저장된 노드의수가 일정 수준 이상 많아지면 해당 해시 버킷을 이진트리로 변환합니다.
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue는 다른 Concurrent Collection과 마찬가지로 Thread-Safe한 구조를 가지고 있습니다.
특징으로는 non-blocking, lock-free queue라는 특징을 가지고 있습니다
이 Class는 큐가 비었을경우에는 null을 리턴하는 특징을 가지고 있습니다.
사용방법은 기존 LinkedList와 유사하여 offer(), poll(), peek()등에 메서드를 지원합니다.
LinkedBlockingQueue
LinkedBlockingQueue는 위에서 말한 ConcurrentLinkedQueue와 다른 특징을 가지고 있습니다.
LinkedBlockingQueue는 Blocking Queue가 링크드 노드로 연결된 구조로 큐에서 꺼내갈 원소가 없을경우에는 해당 스레드는 wait상태에 들어가게 됩니다.
LinkedBlockingQueue 내에 있는 데이터를 가져오기 위해 poll()과 take() 메소드를 제공한다. 이 두 메소드의 차이점은 큐가 비어있을 때, poll 메소드는 null을 리턴하거나 Timeout을 설정할 수 있는 반면에, take 메소드는 꺼낼 수 있는 원소가 있을 때까지 기다린다(waiting).